OPEN RANGE CONSULTING featuring Earth Sense Technology
Providing practical and adaptable tools to rangeland managers, giving them the ability to effect real change and improvements on rangelands.
Healthy Rangelands can change the world with their vast benefits, including crucial wildlife habitat, biodiversity, provide watersheds, carbon sequestration, grazing and forage, renewable and mineral resources, and recreational activities. Range management is challenging because of the lack of tools to appropriately and accurately map the landscape. Managers need spatially rich information to make informed decisions, to make necessary adjustments, and to monitor successes or shortfalls over time. Without these tools it is difficult to measure progress. Open Range Consulting (ORC) has spent 25 years using innovated tools and products that are at a scale and accuracy that can reliably be used by resource managers to improve and protect natural resources and landscapes. ORC's Earth Sense Technology Tools and on the ground validation broaden the rangeland perspective from small expensive samples to robust landscape assessments that offer valid and useful tools which can be used to effect real change and improvements.
Outlined below are examples of some of those tools and how they have helped to provide real change and progress for those using them. Many of these maps are only partial an do not cover the entire expanse of a given project area, they are only used as examples.
Validation
ORC's validation process includes extensive quantifiable verification methods including peer-reviewed articles and patenting, as well as qualitative review by many public and private land managers that have evaluated and compared EST to their experiences. Both the quantitative and qualitative validation suggests that the monitoring results are highly reliable and useful to managers.
An example of quantifiable verification methods is comparing sagebrush cover estimated by remote sensing to independent on the ground line point intercept locations. The figure on the left shows that ORC's sagebrush cover is highly correlated. The figure on the right shows the national level 30 meter sagebrush cover data is much less correlated.
More important than statistical validation is on the ground validation. Every ORC project is validated by the rancher, government specialist or anybody else who is intimately acquainted with the landscape. We are not satisfied with our products until the on the ground person is. These projects sum to 40 million acres and 10,000 miles of stream.
Continuous Cover
Management occurs at a pasture and allotment scale. Often assessments of pastures and allotments are conducted using small and infrequent ground-based plots. These plots are not representative of large geographic areas. Alternatively, pastures and allotments are assessed using 30 meter national level remote sensing products. These products are generally too coarse in detail to make management level decisions. ORC has developed 1 meter resolution remote sensing products that do have enough detail to make management decisions.
ORC's field collection protocol
Continuous cover mapping results in every 1 meter square across the landscape having a percent cover value of bare ground, litter, shrub, perennial and annual grass. This interpolative mapping technique far surpasses historic mapping techniques and creates a precise, fine scale map that gives the land manager a clear representation of what the vegetation conditions are. Currently, national 30m mapping for projects such as these do not provide enough detail at the allotment and pasture level, therefore not meeting the needs of the managers attempting to use them.
These maps identify critical sage-grouse habitat, extreme fire danger, sagebrush cover estimates, bare ground percentage (linked to soil health and productivity) and overall rangeland health.
ORC’s ability to assess rudimentary ground cover conditions over an entire landscape robustly describes and area’s functionality and can detect trends. This allows for the analysis of the relationship between management action (e.g., grazing and land treatments) and conditions.
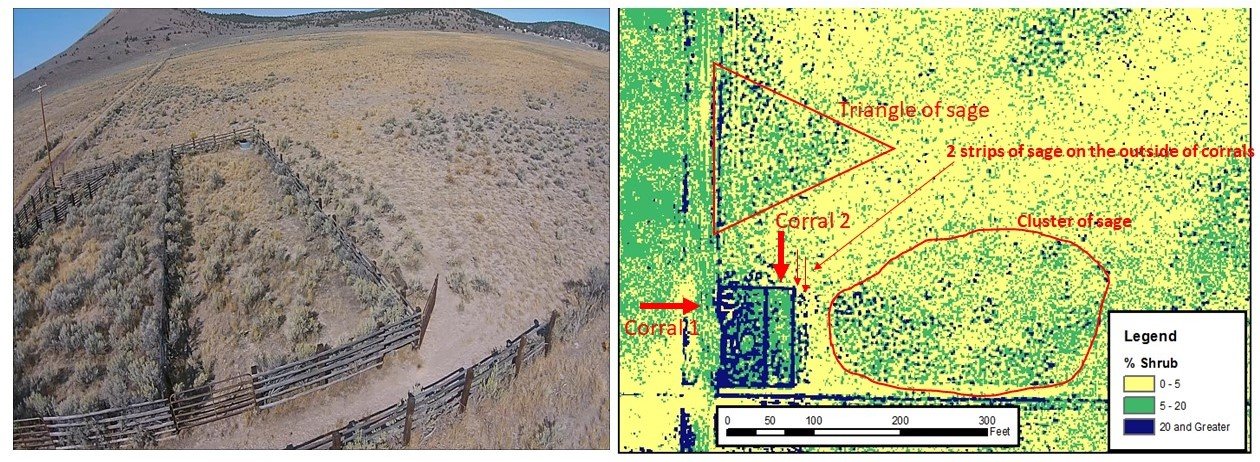
Drone Footage of a Corral with varying amounts of sagebrush
Comparing ORC's sagebrush map to real life photo
Real Picture comparison to the actual amount of sagebrush and how ORC maps sagebrush notice that:
Corral 1 has thicker sagebrush (mapped dark blue)
Corral 2 is lighter sagebrush (shown in green)
Sagebrush triangle beyond the corrals (showing in green)
2 strips of sagebrush along the corral (mapped in blue)
Sagebrush cluster to the right of the corrals (mapped green and blue)
Management Level Dashboards
Large complex geographic datasets are sometimes difficult and unwieldy to use. ORC has developed dashboards that integrate data layers to create user friendly dashboards that answer the questions posed by the infamous table 2.2 (Approved Resource Management Plan Amendment 2016). 30 meter nationwide products available are not suitable and do not meet the needs of the managers trying meet their goals and objectives.